
SSH_config
Intro
Level: needs to be familiar with SSH already.
There are two different sets of configuration files: those for client programs (that is, ssh, scp, and sftp), and those for the server (the sshd daemon).
SSH_config
If you’ve ever used VSCode and SSHed in your instance you’re probably familiar.
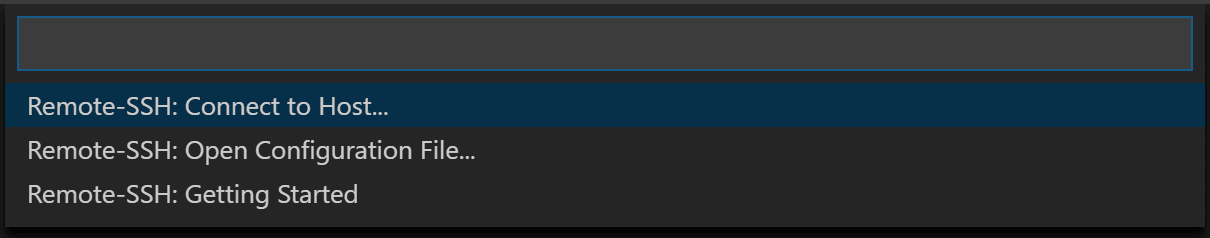
Remote-SSH: Connect to remote host
And you will see your servers IP Address like: 192.168. 255.187 on Hyper V guest VMS or 192.168.122.58 using virualt-manager guest VMS.
if you press control + shift + P or cmd + shift + P in VSCode > Remote-SSH: Open SSH Configuration File
# example
Host Server0172
HostName 192.168.255.187
User guillermo
IdentityFile "/home/guillermo/.ssh/id_ed25519"
Host Server50
HostName 192.168.122.58
User guillermo
IdentityFile "/home/guillermo/.ssh/id_ed25519"
You will see the same addres on host.
But those are actually aliases added to the ssh_config file and not the real IP addresses.
You can give it any name what you want and make it easier to remember and connect your server.
And you can use it in- and outside VSCode.
For example in terminal of your choice, you can do the following command:
ssh Server0172 and you will be connected to the server instantly without remembering every IP Address. This will work when you did use public key authentication.
Don’t forget to add your private key to the agent with the commands:
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
How to configure key-based authentication for SSH: https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/key-based-authentication-ssh